Exclusives

Digital Nirvana: AI, Machine Learning are Revolutionising Media Creation, Distribution
Story Highlights
Cloud-based artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are bringing new levels of accuracy, efficiency, compliance and cost savings to broadcast operations, according to Digital Nirvana.
In the process, the technologies are continuing to transform and accelerate virtually every aspect of content creation and distribution.
During the AI & Automation breakout session “Revolutionising Media Creation and Distribution Using the Science of AI & Machine Learning” at the March 16 Smart Content Summit, Digital Nirvana representatives highlighted real-world examples of media enterprises that are transforming every aspect of their workflows, from subtitles creation to the distribution of content, by implementing the use of AI and ML technologies.
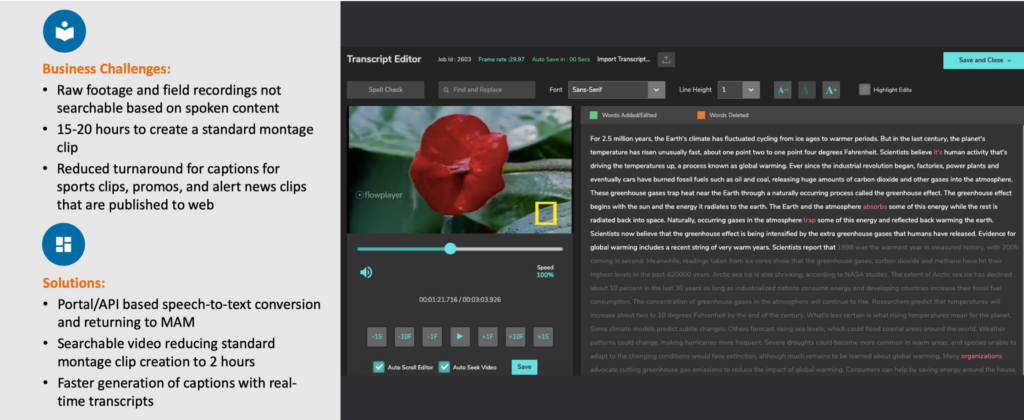
In the area of content acquisition, content contribution and production, it first explored a speech-to-text and captioning workflow that Digital Nirvana co-developed with what Ed Hauber, director of business development at Digital Nirvana, identified as a “well-known entertainment, news and information outlet.”
 “The single biggest driver was time or the extreme lack of time,” he noted, adding: “Like many operating in the news arena, deadlines are tight and time is in short supply. Our client had a two-hour window in which to ingest, edit, caption and deliver its finished product to” an over-the-top (OTT) provider in the expected format.
“The single biggest driver was time or the extreme lack of time,” he noted, adding: “Like many operating in the news arena, deadlines are tight and time is in short supply. Our client had a two-hour window in which to ingest, edit, caption and deliver its finished product to” an over-the-top (OTT) provider in the expected format.
Digital Nirvana used automatic speech recognition (ASR) technology to help solve that challenge, according to Russell Vijayan, head of AI products and services at Digital Nirvana.
Digital Nirvana provided the client with the ability to go to specific places in a piece of video and, by clicking on search terms, find all the content they needed “much faster,” allowing it to produce content within the timeline that they were given, explained Vijayan.
“The second challenge for that client was the need to deliver accurately captioned content within the time frame allotted” to it, Hauber said. Adding to the challenge was the need to deliver content in full compliance with the OTT service provider’s strict style guidelines for captioning and subtitles, he noted.
The client did not have time to use a turnkey, third-party resource to send out the content, have it captioned and turned around, according to Hauber.
Digital Nirvana used a combination of technologies to overcome that challenge, Vijayan explained. Digital Nirvana created transcripts that could be converted into subtitles or captions quickly.
It then applied a layer of natural language processing (NLP) that would help split the captions so that the user didn’t need to spend much time making any changes, he said. The captions created using this AI-based system have 98-99% accuracy, so very few corrections need to be made, he added.
The third challenge was something that Digital Nirvana is increasingly seeing: Operators needs to localise their content – specifically the captions – into other languages, in this case, English and Latin American Spanish, Hauber said.
In this case, Digital Nirvana needed to create Spanish captions after the English captions were created, Vijayan said, adding it created a set of algorithms that would dictate how much content needed to be translated to get a much more accurate result. The second use case was to import existing English captions and then quickly translate them to other languages, he added.
 Moving on to distribution and video metadata, Hauber briefly discussed applications of AI in the content delivery space, “primarily the mining of insights from within content, which allow our clients to analyse and report on production product placements, perform ad classification and uncover potential compliance issues such as identification of explicit content.”
Moving on to distribution and video metadata, Hauber briefly discussed applications of AI in the content delivery space, “primarily the mining of insights from within content, which allow our clients to analyse and report on production product placements, perform ad classification and uncover potential compliance issues such as identification of explicit content.”
Hauber pointed to use cases with two multichannel video programming distributors (MVPDs). In both cases, they had original content but most of the distribution was other peoples’ content — 300-400 channels worth of it, he said, noting both companies used compliance logging and monitoring technology to record distributed content that had been aired. The goal was extracting data from the distributed content, he noted.
The technology can be used for product placement and to replace one product with another in a piece of video content. As an example, Vijayan noted that when a refrigerator is opened on the screen, there may be a Coke in there and a company might want to change it to Pepsi.
Digital Nirvana solutions provide: Customised video-based metadata for better searchability; the ability to accurately identify spots based on content; identify and replace brands within content based on consumer data; and a reduction of effort in identifying explicit content, according to the company.
Click here to access video of the presentation.
Click here to download the presentation.
The Smart Content Summit was produced by MESA and the Smart Content Council, and was sponsored by Microsoft Azure, Whip Media Group, Richey May Technology Solutions, BeBanjo, Digital Nirvana, Softtek, 24Notion, EIDR, The Quorum and Signiant.









